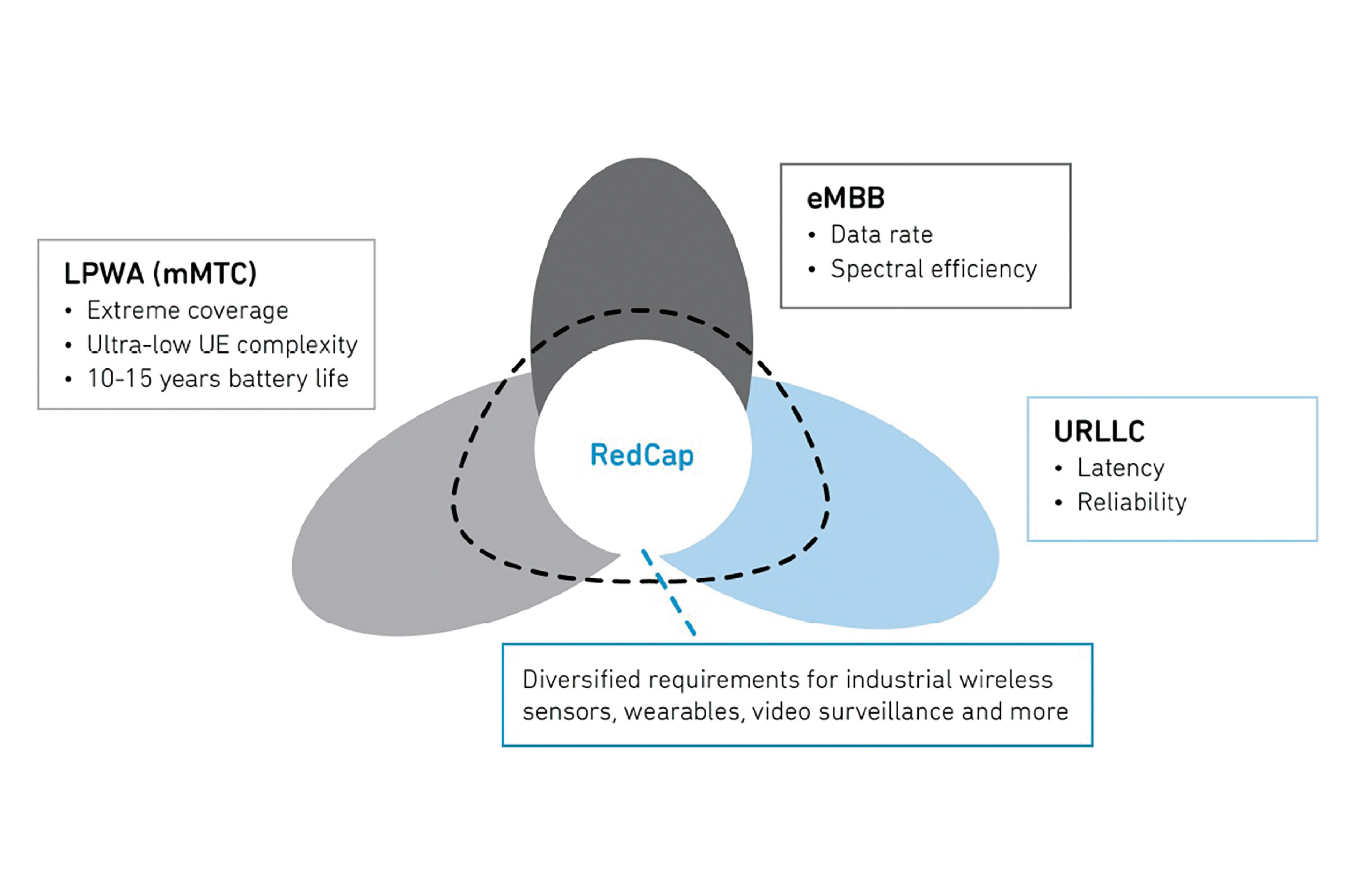
Reduced Capability New Radio (NR-REDCAP) will address Mid-Speed Smart IoT applications with connectivity demands higher than LTE-M/NB-IoT can provide but not requiring critical IoT services such as mmWave or ultra-low latency.
Over the past few years, with the increasing demand for Low-Power Wide-Area Networks (LPWANs) for industrial applications, a couple of cellular-based technologies have emerged as the solution for many deployments: LTE CatM and NB-IoT.
Both technologies allow for massive IoT and wide-area connectivity on 4G LTE networks, enabling millions of small devices such as sensors and actuators that require basic connectivity, wide-area coverage, and must operate on batteries or limited power.
NB-IoT is designed to keep power consumption at a minimum and operate on the sub-GHz spectrum, including unlicensed bands. At the same time, LTE-M uses higher bands and also supports SMS and voice applications. Both NB-IoT and LTE-CatM (a.k.a. eMTC) fulfill the IMT-2020 requirements for mMTC and can be certified as 5G technologies.
With the advent of 5G networks, a new horizon of possibilities has emerged as the New Radio allows for much higher bandwidth, especially on millimeter-wave frequencies, and ultra-low latency, which is required for critical applications such as remote operations and autonomous vehicles.
For many industrial applications, however, there is a gap between LPWANs and critical IoT. Many applications will require more bandwidth than CatM and NB-IoT can provide, but not the higher speeds and low latency that critical services need.
The easy solution for some users would be to connect directly to an existing LTE network on a standard mobile package and use data at LTE speeds as needed. But for many industrial uses requiring connecting hundreds or thousands of devices, it becomes expensive and problematic at least.